School Projects – 5 Innovative Ideas for Creations
Craftsmanship in school projects is a multi-faceted concept that combines the art of creating with precision, attention, and a deep appreciation for quality. In educational settings, integrating craftsmanship into projects not only enriches the learning experience but also instills in students a sense of pride and accomplishment in their work. It’s a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application, allowing students to express their creativity while developing tangible skills. This opening will delve into why incorporating craftsmanship into school projects is beneficial, touching on skill development, enhanced creativity, and the fostering of patience and attention to detail.
The concept of craftsmanship transcends traditional art and woodwork; it encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including technology, science, and digital arts. It encourages students to approach projects with a meticulous eye, ensuring that every detail is considered and every finish is executed with precision. This meticulousness in execution not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of projects but also their functionality and longevity. Moreover, the integration of craftsmanship into school projects promotes a culture of excellence and dedication. It teaches students the value of hard work and perseverance, as achieving high-quality results often requires multiple iterations and continuous improvement. This process helps students develop a growth mindset, where challenges are seen as opportunities for learning and development. Finally, school projects with craftsmanship prepare students for the real world, where these skills are highly valued. Whether in the arts, sciences, or any other field, the ability to produce work that is both functional and well-crafted is a significant asset. By fostering these skills early on, educators are helping shape future professionals who appreciate quality and detail in their work.
The Decline of Craftsmanship in Modern Education
The digital age has brought about significant changes in how we live, work, and learn. With the increasing reliance on technology in education, there has been a noticeable shift away from hands-on, craft-based learning. This transition has led to a decline in opportunities for students to engage in school projects that require the development and application of craftsmanship skills. The implications of this shift are far-reaching, affecting not only the quality of students’ work but also their overall learning experience. The decline in craftsmanship in education can be attributed to several factors, including the emphasis on standardized testing and the prioritization of digital literacy over traditional skills. While these are important aspects of contemporary education, they should not overshadow the value of craftsmanship. Skills such as fine motor control, spatial awareness, and the ability to work with materials are increasingly being sidelined, leading to a generation of students who may lack the ability to create and fix things by hand.
This trend is concerning for educators who recognize the importance of a balanced education that includes both digital and manual skills. The decline in craftsmanship not only impacts the arts but also fields like engineering and science, where hands-on skills are for innovation and problem-solving. As students spend more time interacting with screens, their opportunities to engage with physical materials and develop their craftsmanship are diminishing. Addressing this decline requires a conscious effort from educators, parents, and policymakers to reintegrate craftsmanship into the curriculum. This could involve more project-based learning, where students are tasked with creating tangible products, or the opening of maker spaces in schools, where students have access to tools and materials to create. By valuing and promoting craftsmanship in education, we can ensure that students develop a well-rounded set of skills that will serve them well in their future endeavors.
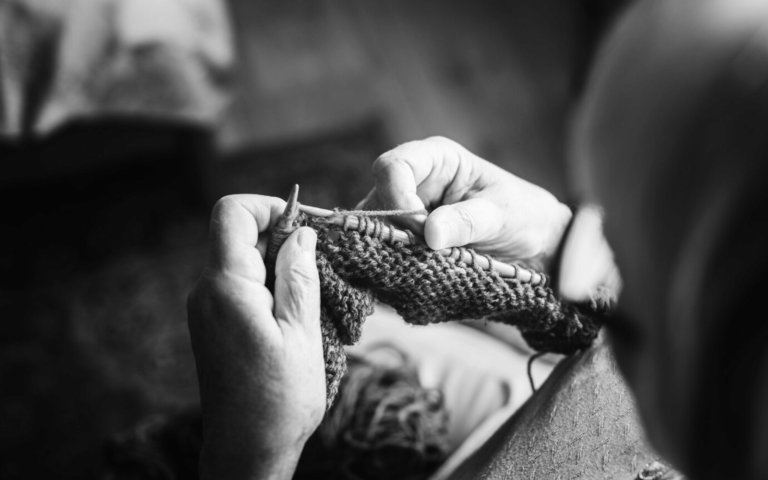
The Link Between Craftsmanship and Fine Motor Skills
School projects that incorporate craftsmanship play a role in the development of fine motor skills. These skills, which involve the coordination of small muscle movements in the hands and fingers, are essential for performing a wide range of tasks, from writing and drawing to manipulating tools and materials. By engaging in projects that require precision and attention to detail, students can significantly improve their dexterity and control. The relationship between fine motor skills and craftsmanship is symbiotic. As students undertake projects that demand precision, such as woodworking, sewing, or detailed art projects, they not only produce work of higher quality but also enhance their fine motor skills. This improvement is due to the repetitive nature of the tasks involved, such as cutting, threading, or applying paint with accuracy, which strengthens the muscles in the hands and improves coordination.
Furthermore, the development of fine motor skills through craftsmanship has broader implications for students’ academic and personal lives. Improved dexterity can lead to better handwriting, more efficient use of technology, and a greater ability to perform everyday tasks with ease. Additionally, the sense of achievement that comes from learning these skills can boost students’ confidence and encourage them to take on more challenging projects. To foster the development of fine motor skills, educators should incorporate a variety of craft-based projects into their curriculum. These projects should be designed to challenge students at different skill levels, ensuring that all students have the opportunity to improve their dexterity and precision. By prioritizing craftsmanship in school projects, educators can help students develop essential skills that will benefit them throughout their lives.
Incorporating Craftsmanship into Art Projects
Art projects offer a perfect platform for incorporating craftsmanship into the curriculum. These projects allow students to their creativity while paying close attention to detail, technique, and quality of planning. Whether working with paint, clay, textiles, or mixed media, students can learn the value of patience, precision, and persistence in creating art that is both beautiful and well-crafted. One of the key benefits of focusing on craftsmanship in art projects is the opportunity for students to develop a deep appreciation for the materials and tools they use. Understanding the properties of different mediums and how to use them to achieve desired outcomes is a fundamental aspect of craftsmanship. This knowledge not only enhances the quality of their work but also fosters a sense of respect and responsibility towards their resources.
Additionally, art projects with an emphasis on craftsmanship challenge students to push beyond their initial ideas and strive for excellence in their planning. This iterative process, where students plan, create, evaluate, and refine their work, mirrors the creative process used by professional artists and designers. It teaches students that great work often requires revision and adaptation, encouraging a growth mindset and resilience in the face of obstacles. Educators can support the development of craftsmanship in art projects by setting clear expectations for quality and providing constructive feedback throughout the creation process. This guidance helps students understand the standards they should aspire to and the steps they can take to improve their work. Moreover, showcasing exemplary projects can inspire students to take pride in their craftsmanship and motivate them to achieve higher standards in their own work. By integrating craftsmanship into art school projects, educators can provide students with a holistic learning experience that combines technical skill development with creative expression. This approach not only enriches students’ education but also prepares them for future attention where creativity, precision, and attention to detail are highly valued.
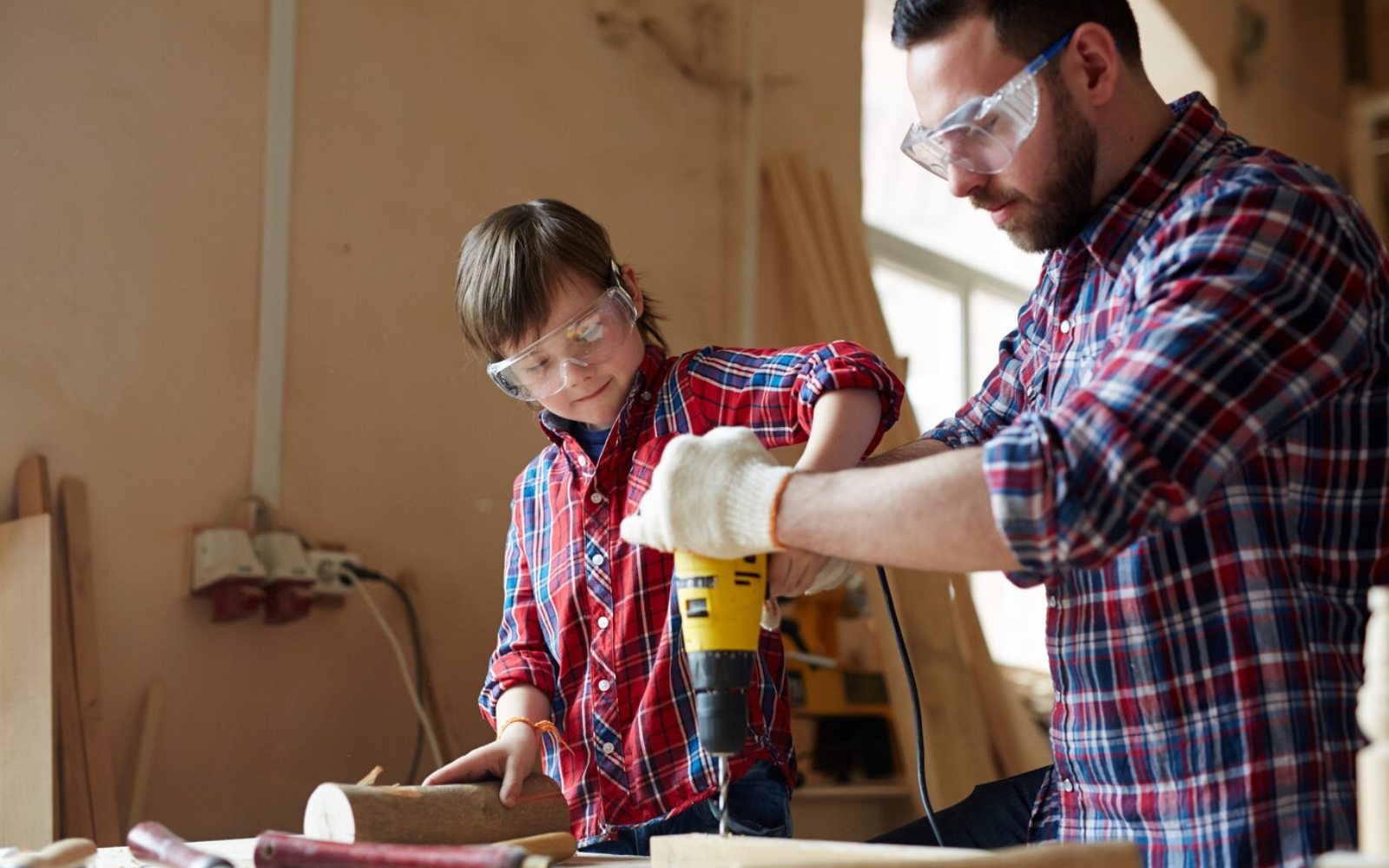
Woodworking: A Pathway to Developing Craftsmanship
Woodworking projects offer a tangible and rewarding way to develop craftsmanship among students. These projects, which can range from simple constructions to more complex creations, teach valuable skills such as measuring, cutting, sanding, and finishing. Through woodworking, students gain hands-on experience with tools and materials, learning to transform raw wood into functional and aesthetically pleasing items. The process of planning and executing a woodworking project from start to finish instills in students a sense of responsibility and ownership over their work. This journey, fraught with challenges and learning opportunities, allows students to experience firsthand the satisfaction of creating something tangible. It teaches them the importance of following detailed plans, the patience required in crafting, and the pride that comes from producing a well-made product.
Woodworking projects offer a tangible and rewarding way to develop craftsmanship among students, these school projects, which can range from simple constructions to more complex creations, teach valuable skills such as measuring, cutting, sanding, and finishing. Through woodworking, students gain hands-on experience with tools and materials, learning to transform raw wood into functional and aesthetically pleasing items. The process of planning and executing a woodworking project from start to finish instills in students a sense of responsibility and ownership over their work. This journey, fraught with challenges and learning opportunities, allows students to experience firsthand the satisfaction of creating something tangible. It teaches them the importance of following detailed plans, the patience required in crafting, and the pride that comes from producing a well-made product.
Moreover, woodworking projects can be tailored to match the skill level of the students, allowing for progressive learning. Beginners might start with simple projects like picture frames or birdhouses, which introduce basic techniques and tools. As students’ skills advance, they can tackle more complex projects that require precision and creativity, such as furniture making or carving. This progression not only builds their technical skills but also encourages critical thinking and problem-solving. Finally, woodworking as a pathway to developing craftsmanship in school projects offers an invaluable lesson in sustainability and resourcefulness. Students learn to appreciate the material they work with, understanding the importance of minimizing waste and maximizing utility. They discover the significance of quality workmanship in creating durable items, countering the throwaway culture prevalent in society today. Incorporating woodworking into the curriculum is a strong way to cultivate craftsmanship among students. It not only equips them with practical skills but also fosters a deep appreciation for the art of making, encouraging them to pursue excellence in all their creative endeavors.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Craftsmanship
In today’s digital age, technology plays a significant role in enhancing craftsmanship in school projects. While traditional craftsmanship focuses on manual skills and the use of physical tools, the integration of digital tools can expand the possibilities for creativity and precision. From design software to digital fabrication tools like 3D printers and laser cutters, technology offers students new ways to conceptualize and execute their projects with a high degree of accuracy and intricacy. One of the key advantages of using technology in craftsmanship school projects is the ability to experiment with designs before physical creation. Software applications allow students to visualize their projects, adjust dimensions, and experiment with different materials and finishes. This digital planning phase can lead to a deeper understanding of the design process and prevent costly mistakes in the physical production phase.
Furthermore, technology can democratize access to complex manufacturing techniques that were once only available to professionals. For example, 3D printing enables students to create complex shapes and structures that would be difficult, if not impossible, to achieve with traditional hand tools. Similarly, laser cutters can produce precise cuts and engravings on a variety of materials, allowing for intricate designs and finishes. However, the use of technology in crafting school projects should complement, rather than replace, traditional craftsmanship skills. The tactile experience of working with materials directly, the understanding of physical properties, and the development of hand-eye coordination are all critical aspects of craftsmanship that technology alone cannot replicate. Educators should strive to find a balance, leveraging technology to enhance the learning experience while ensuring that students remain grounded in the fundamental principles of craftsmanship. By thoughtfully integrating technology into craftsmanship projects, educators can provide students with a comprehensive skill set that prepares them for the future. Students learn not only how to design and create with their hands but also how to utilize modern tools and technologies to bring their visions to life in innovative ways.
Case Studies: Successful School Projects with Craftsmanship
Case studies of successful school projects with craftsmanship can provide valuable insights into how these initiatives can be implemented and the benefits they offer to students. Across the globe, educators have integrated craftsmanship into their curriculum in various ways, from woodworking and metalworking to digital fabrication and textile arts. These case studies highlight the creativity, problem-solving, and technical skills students can develop through hands-on school projects.
One notable example is a high school woodworking program that tasks students with designing and building their own furniture. This project combines traditional woodworking techniques with elements of design thinking, requiring students to plan their school projects, consider the functionality and aesthetics of their pieces, and execute their plans with precision. The success of this program lies in its ability to engage students in a comprehensive learning process, from conceptualization to creation, resulting in tangible products that students can take pride in. Another example is an art class that focuses on textile arts, where students learn about different materials, weaving techniques, and patterns. This project not only teaches students about the history and cultural significance of textile arts but also allows them to apply this knowledge in creating their own textile pieces. The attention to detail and the manual dexterity required for weaving reinforce the principles of craftsmanship while fostering a connection to traditional crafts.
A third case study involves a STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) project that incorporates digital fabrication tools. Students design and create innovative products, using 3D printers and laser cutters to bring their ideas to life. This project demonstrates how craftsmanship can be applied in a modern context, blending traditional design principles with cutting-edge technology to solve real-world problems. These case studies illustrate the versatility of craftsmanship in education and its applicability across various disciplines. By incorporating school projects that emphasize craftsmanship, educators can provide students with a rich learning experience that promotes creativity, critical thinking, and practical skills. Moreover, these projects prepare students for the future by equipping them with a blend of traditional and modern skills that are highly valued in today’s workforce.
How to Overcome Challenges in Teaching Craftsmanship
Teaching craftsmanship in schools comes with its set of challenges, from logistical issues such as funding and space to curricular constraints that prioritize academic over practical skills. However, these challenges can be overcome with creative solutions and a commitment to providing students with meaningful, hands-on learning experiences. One of the primary challenges is securing the resources needed for craftsmanship projects. Materials, tools, and equipment can be costly, but schools can analyse partnerships with local businesses, grants, and community fundraising efforts to obtain the necessary resources. Additionally, repurposing and recycling materials can be a cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach to resource acquisition.
Another challenge is integrating craftsmanship projects into the existing curriculum. Educators can address this by highlighting the cross-curricular benefits of craftsmanship, such as its application in science, mathematics, and history. By demonstrating how these school projects enhance students’ understanding of academic concepts through practical application, teachers can make a compelling case for the inclusion of craftsmanship in the curriculum. The lack of trained instructors can also be a barrier to teaching craftsmanship. Professional development opportunities, workshops, and collaboration with artisans and craftspeople from the community can help teachers acquire the skills and confidence to lead these school projects. Moreover, incorporating student-led teaching, where more experienced students mentor their peers, can foster a collaborative learning environment.
Finally, addressing safety concerns is for any program involving tools and equipment. Implementing comprehensive safety protocols, providing proper training for students and staff, and ensuring close supervision during project work can mitigate s and create a safe learning environment. Despite these challenges, the benefits of integrating craftsmanship into education are clear. With creativity, collaboration, and a focus on student-centered learning, schools can successfully incorporate craftsmanship projects into their curriculum, providing students with valuable skills and enriching their educational experience.
Promoting Teamwork Through Group Craftsmanship Projects
In today’s educational environment, the emphasis on individual achievement often overshadows the significant benefits of collaborative learning. One of the most effective ways to foster a sense of community and shared purpose in schools is through group craftsmanship projects. These initiatives not only bring students together to work towards a common goal but also help them develop valuable interpersonal skills. By engaging in projects that require collective problem-solving and creativity, students learn the importance of communication, patience, and flexibility—skills essential for their future professional and personal lives.
Group projects in craftsmanship specifically provide a platform where each participant can contribute their unique skills and perspectives, leading to a richer and more comprehensive project outcome. For instance, while constructing a model ecosystem, students can divide tasks such as design, building, and decoration among themselves, depending on their individual strengths and interests. This division of labor not only makes the project more manageable but also gives each student a sense of ownership and responsibility for the success of the overall project.
Moreover, working in groups allows students to witness firsthand the challenges of coordinating with others, adapting to different working styles, and resolving conflicts amicably. These real-world interactions are crucial for preparing students to navigate complex social and professional landscapes in their future. Educators can facilitate these projects by providing clear guidelines, necessary materials, and periodic supervision, ensuring that the learning objectives are met while maintaining an atmosphere of creativity and inclusivity. Ultimately, group craftsmanship projects not only enrich the educational experience by producing tangible, collaboratively created artifacts but also cultivate a collaborative spirit, preparing students to work effectively in team settings beyond the classroom.
See More At: woolen8wonders.com